Resources to run great sports programs
Top Games: Reaction: Stop Disc Cones from Falling down a Post
Continue Reading...
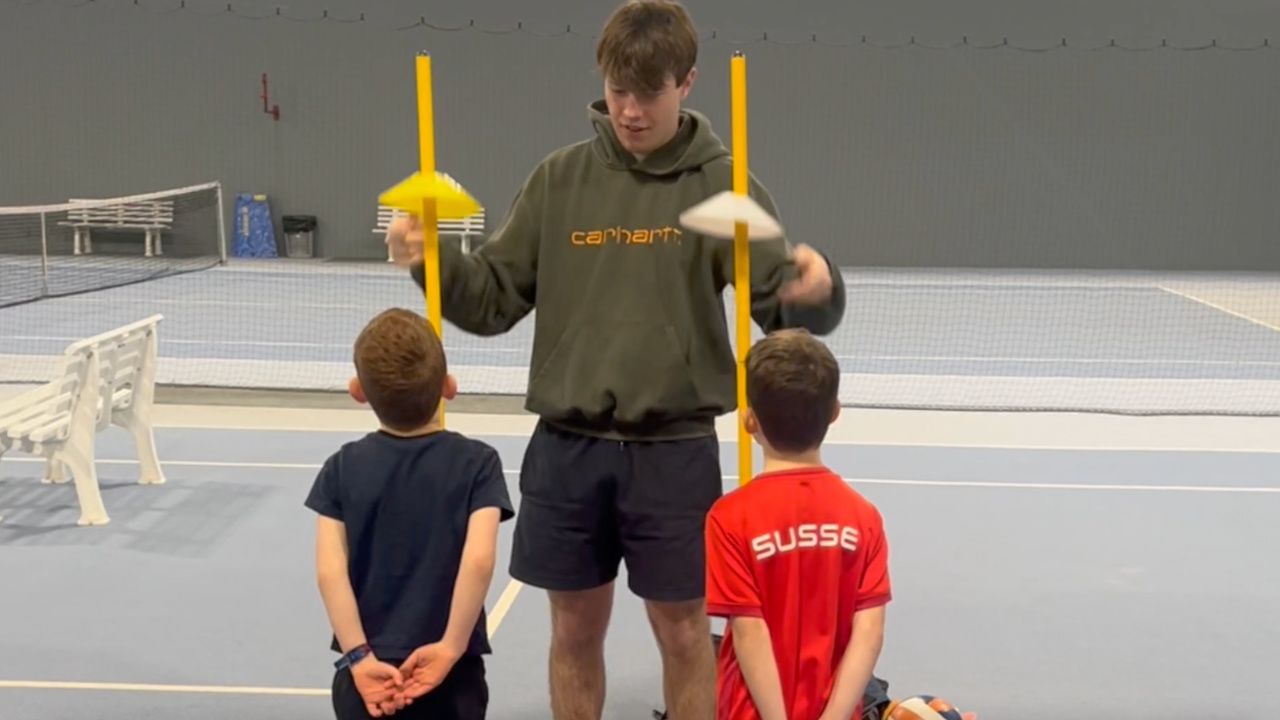
Challenge 1: Stop Disc Cones from Falling down a Post
- Put one disc cone upside down through ...
Top Games: Balance: Poisonous Mushroom Hunt
Continue Reading...
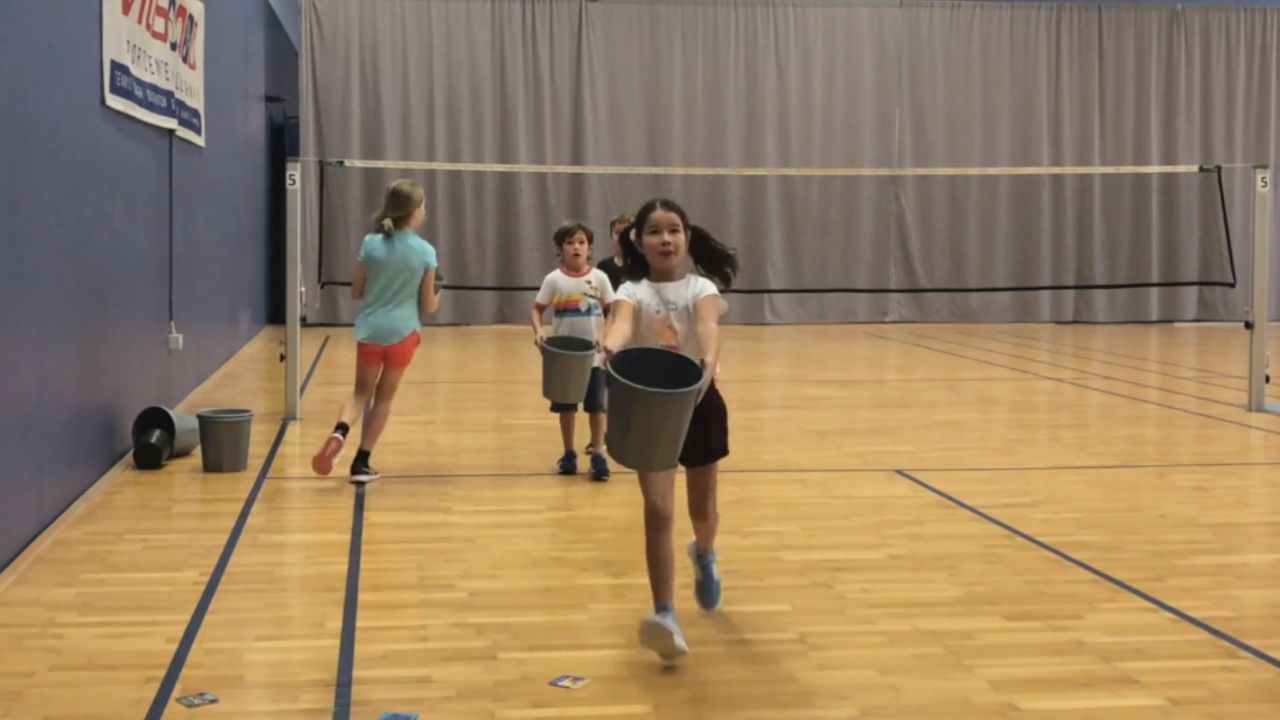
Challenge 1: Poisonous Mushroom Hunt
- Each child gets a small bucket to collect mushrooms. ...
Top Games: Rhythm: Hoop Dance
Continue Reading...
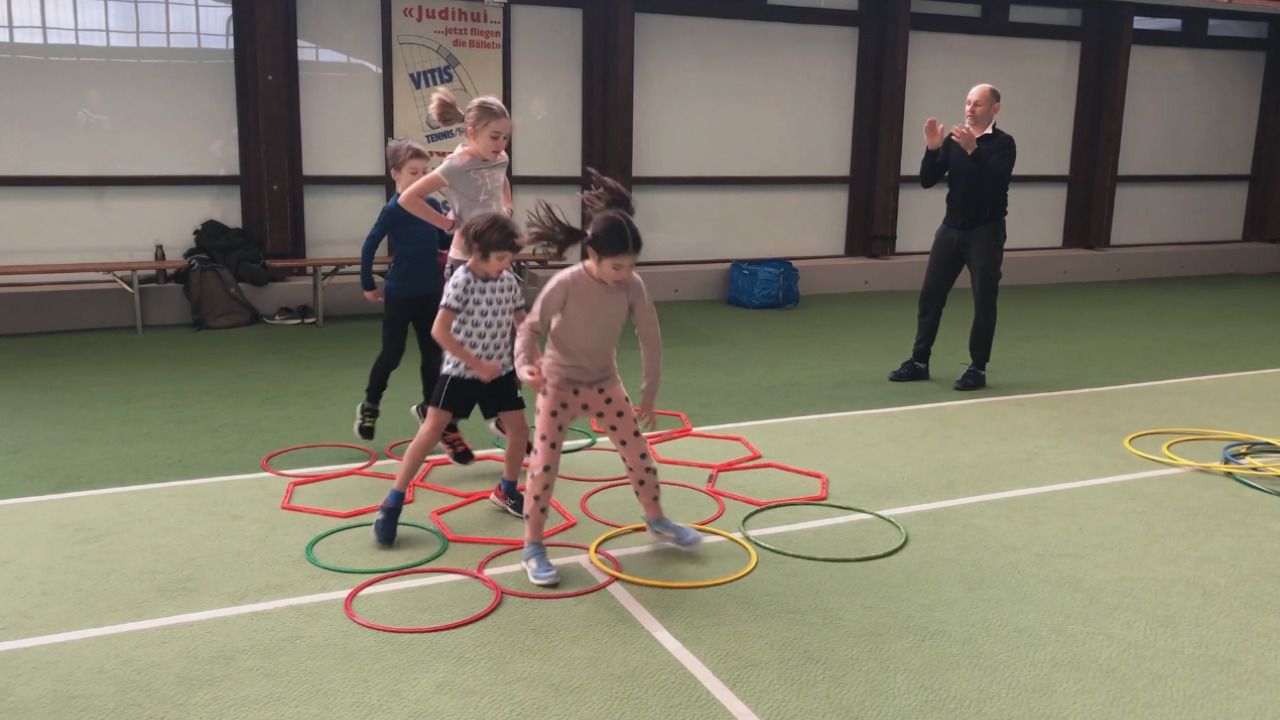
Challenge 1: Hoop dance
- Put up a rectangle made up of hoops on the floor.
- The coach gives ...
Top Games: Hand-eye Coordination: Easy Drink Coaster Spin
Continue Reading...
Game 1: Catch spinning drink coasters
- Flip the drink coasters (or use pieces of card box) ...
Top Games: Physical Activity: The Safe House
Continue Reading...
Game 1: The safe house
- You need some play huts as shown.
- Children line up on one end of th ...
Top Games: Hand-Eye Coordination: The Cone Tree
Continue Reading...
Game 1: Cone Tree
- Put up a ladder, the Christmas tree, at a wall to keep it from falling do ...
Top Games: Hide Your Hat
Continue Reading...
Game 1: Hide your Hat
- Each child holds a disc cone of a different color and tries to hide i ...
Top Games: Fishing with Running
Continue Reading...
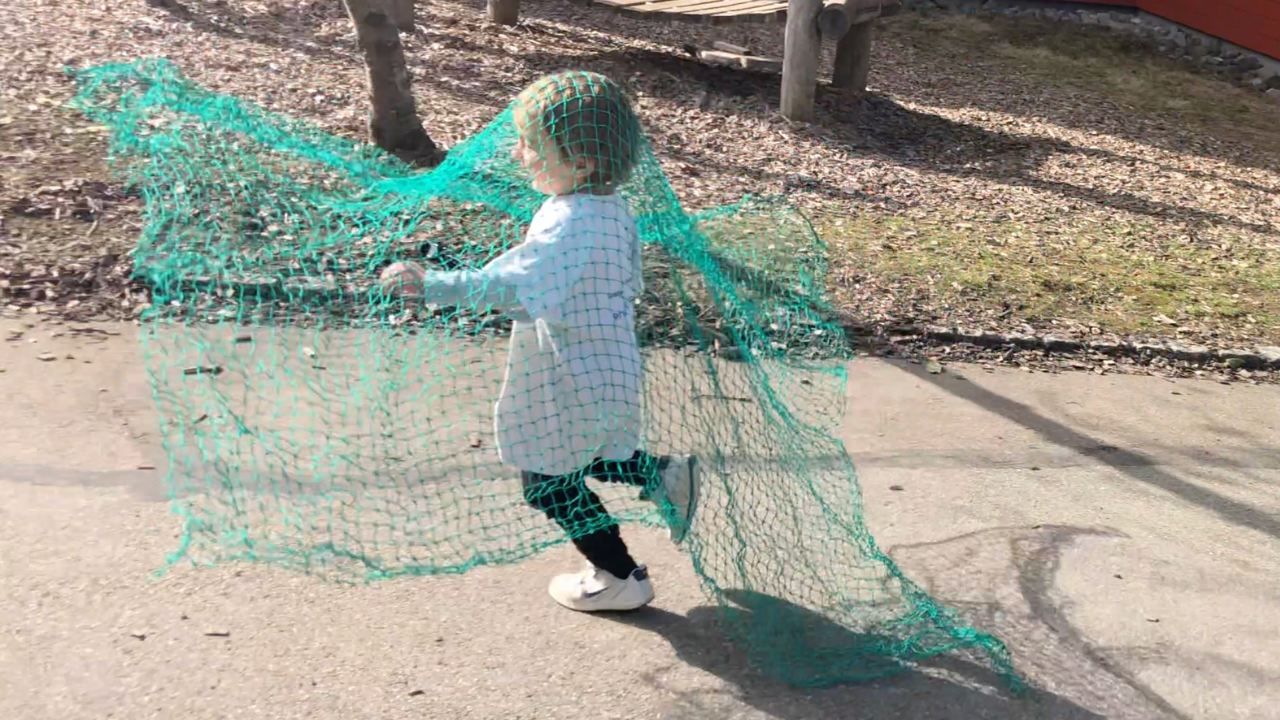
Game 1: Fishing Net with Running
- Children are all fish, swimming in a defined playing field...
Top Games: Soccer Twin Relay
Continue Reading...
Game 1: Soccer Twin Relay
- Each child has 2 balls each, the soccer twins, and on command has ...
Top Games: Jump over Rolling Log
Continue Reading...
Game 1: Jump over Rolling Log
- Push a card box tube, foam roller, or other round stick back ...
Top Games: The Streets of Mumbai with Turning
Continue Reading...
Challenge 1: The Streets of Mumbai with Turning
- One child or the coach is designated the le ...
A Look Inside the 4 Motor Skill Learning Curricula for 3-4, 4-5, 5-6, 6-7 Year-Olds
Continue Reading...
A Look Inside the Motor Skill Learning Curricula for Physical Education in Preschool and Kindergarte...